Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycosidic Bond
A glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that connects two monosaccharides through a dehydration reaction, resulting in the formation of a disaccharide. In cellobiose, this bond specifically links the anomeric carbon of one glucose unit to the hydroxyl group of another glucose unit, creating a β(1→4) linkage.
Recommended video:
Glycosidic Linkage Formation Concept 1
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are carbohydrates formed by the combination of two monosaccharides through glycosidic bonds. Cellobiose, composed of two glucose molecules, is an example of a disaccharide that plays a significant role in the structure of cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls.
Recommended video:
Types of Disaccharides Concept 1
Monosaccharide Classification
Monosaccharides are classified based on the number of carbon atoms they contain and the functional groups present. In the case of cellobiose, both constituent monosaccharides are hexoses, specifically glucose, which is a six-carbon sugar. Understanding this classification helps in analyzing the properties and reactions of carbohydrates.
Recommended video:
Reduction of Monosaccharides Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution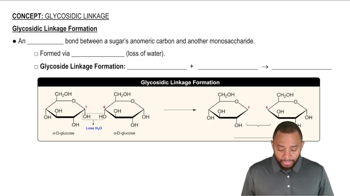



 1:44m
1:44m