Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Catabolism
Catabolism refers to the metabolic process where complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. In the context of fats, catabolism involves the breakdown of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol, which can then be further oxidized to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amino Acid Catabolism Concept 1
Energy Investment Phase
The energy investment phase is the initial stage of a metabolic pathway where energy, often in the form of ATP, is consumed to activate substrates. In fat catabolism, this phase includes the activation of fatty acids to acyl-CoA, which requires ATP, setting the stage for subsequent energy-releasing reactions.
Recommended video:
Beta-Oxidation
Beta-oxidation is the metabolic process by which fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH2. This process yields a significant amount of energy, as the acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, leading to further ATP production, thus exemplifying the large payoff after the initial energy investment.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution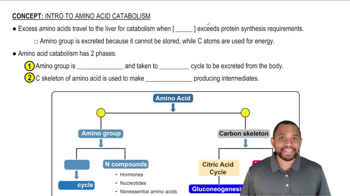


 1:3m
1:3m