Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). They are unsaturated compounds, meaning they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms. The presence of the double bond gives alkenes unique reactivity, making them important in various chemical reactions, including addition reactions where new atoms or groups can be added across the double bond.
Recommended video:
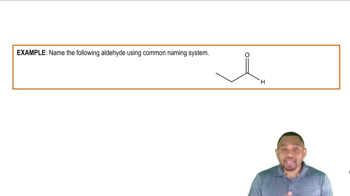
Aldehydes
Aldehydes are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of a carbon chain. The general formula for aldehydes is RCHO, where R represents a hydrocarbon group. Aldehydes are known for their reactivity, particularly in oxidation reactions, where they can be converted into carboxylic acids, and in nucleophilic addition reactions due to the electrophilic nature of the carbonyl carbon.
Recommended video:
Naming Aldehydes Example 2
Ketones
Ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) located within a carbon chain, specifically between two carbon atoms. The general formula for ketones is RC(=O)R', where R and R' can be the same or different hydrocarbon groups. Ketones are important in organic chemistry due to their role in various reactions, including nucleophilic addition and oxidation, and they are commonly found in solvents and as intermediates in synthesis.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:49m
1:49m