Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exothermic Reaction
An exothermic reaction is a chemical process that releases energy in the form of heat to its surroundings. This release of energy often results in an increase in temperature of the reaction mixture. Common examples include combustion reactions, such as burning wood or fossil fuels, where energy is released as heat and light.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Exergonic Reaction
An exergonic reaction refers to a process that releases free energy, making it thermodynamically favorable. This type of reaction is characterized by a negative change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG < 0), indicating that the products have lower energy than the reactants. Exergonic reactions can occur in various contexts, including biochemical pathways like cellular respiration.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Energy Transfer in Reactions
Understanding energy transfer is crucial for distinguishing between exothermic and exergonic reactions. While exothermic reactions specifically focus on heat release, exergonic reactions encompass a broader range of energy changes, including work done by the system. Both concepts highlight how energy is transformed during chemical processes, impacting reaction spontaneity and equilibrium.
Recommended video:
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution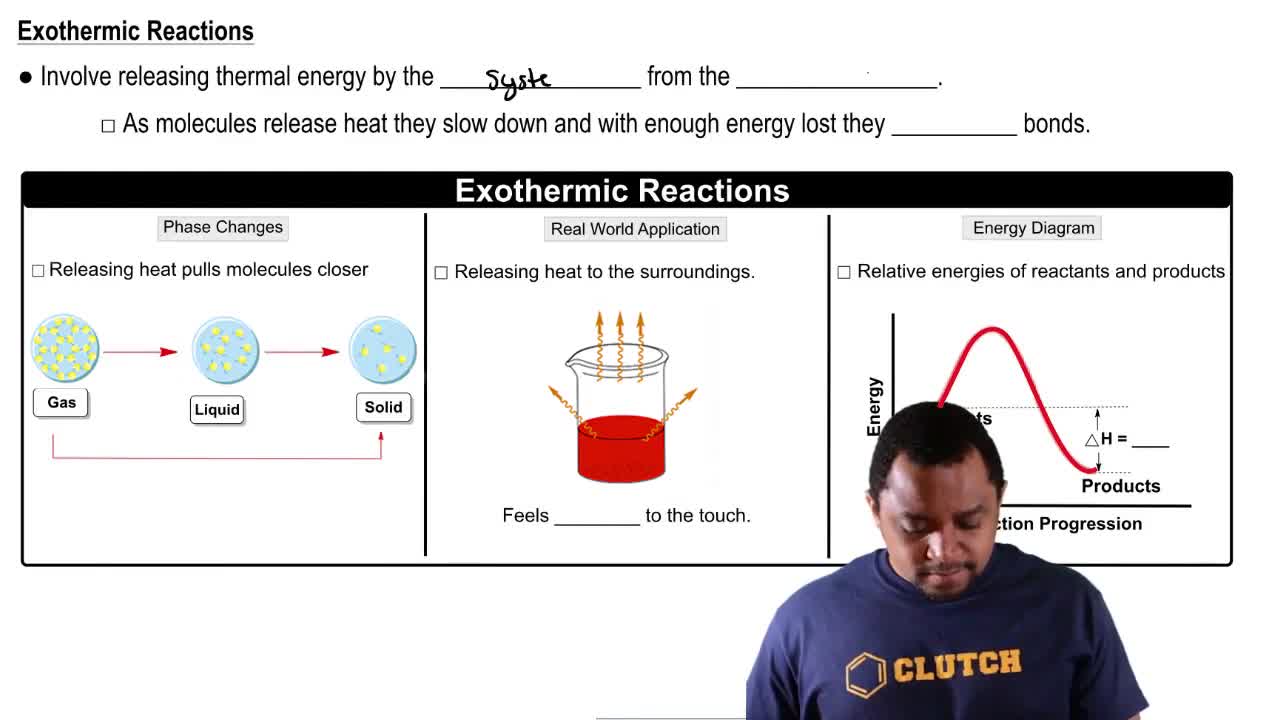



 0:46m
0:46m
