Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enzyme Substrate Specificity
Enzyme substrate specificity refers to the unique ability of an enzyme to bind to a specific substrate, which is the molecule upon which the enzyme acts. This specificity is determined by the enzyme's active site, where the substrate fits like a key in a lock. Understanding this concept is crucial for identifying the correct substrate for any given enzyme.
Recommended video:
Enzyme-Substrate Complex Concept 1
Maltase Function
Maltase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose, a disaccharide sugar, into two glucose molecules. This reaction is essential in carbohydrate digestion, particularly in breaking down starches into simpler sugars that can be absorbed by the body. Knowing the function of maltase helps in identifying its substrate.
Recommended video:
Substrate of Maltase
The substrate of maltase is maltose, which is formed from the breakdown of starch by amylase. When maltose is present, maltase facilitates its conversion into glucose, which is a primary energy source for cells. Recognizing maltose as the substrate is key to understanding maltase's role in metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Enzyme-Substrate Complex Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution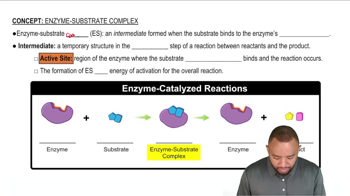



 :39m
:39m