Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Globular Proteins
Globular proteins are spherical in shape and are typically soluble in water. They play crucial roles in biological processes, including enzyme activity, transport, and immune responses. Their structure allows for a diverse range of functions, as the arrangement of amino acids influences their interactions and stability.
Recommended video:
Digestion of Proteins Concept 1
Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Interactions
In globular proteins, amino acids can be classified as hydrophobic (water-repelling) or hydrophilic (water-attracting). Hydrophobic residues tend to be found in the interior of the protein, away from water, while hydrophilic residues are often located on the surface, interacting with the aqueous environment. This distribution is crucial for the protein's stability and function.
Recommended video:
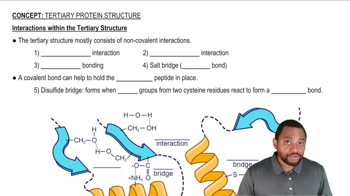
Interactions within the Tertiary Structure Concept 2
Protein Folding
Protein folding is the process by which a linear chain of amino acids acquires its functional three-dimensional structure. This process is driven by various interactions, including hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and van der Waals forces. Proper folding is essential for the protein's functionality, and misfolding can lead to diseases.
Recommended video:
Tertiary Protein Structure Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:7m
2:7m