Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ester Hydrolysis
Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where an ester reacts with water to form an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. This reaction can occur under acidic or basic conditions, with base hydrolysis often referred to as saponification. Understanding this process is crucial for predicting the products formed when an ester is treated with water.
Recommended video:
Acid-Catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis Concept 1
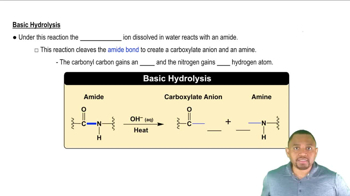
Base Hydrolysis
Base hydrolysis involves the reaction of an ester with a strong base, typically sodium hydroxide (NaOH), leading to the formation of a carboxylate salt and an alcohol. This reaction is significant in organic chemistry and is commonly used in the production of soaps from fats and oils. The presence of the base accelerates the reaction and alters the products compared to acid-catalyzed hydrolysis.
Recommended video:
Basic Hydrolysis Concept 2
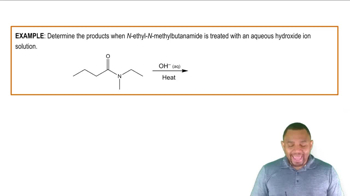
Products of Hydrolysis
The products of base hydrolysis of an ester include a carboxylate ion and an alcohol. For example, when ethyl acetate undergoes base hydrolysis, it yields sodium acetate and ethanol. Recognizing these products is essential for understanding the implications of ester reactions in various chemical processes, including industrial applications and biological systems.
Recommended video:
Basic Hydrolysis Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution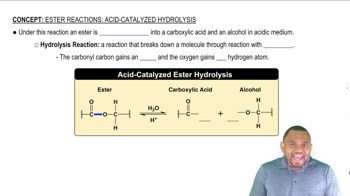

 1:25m
1:25m