Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
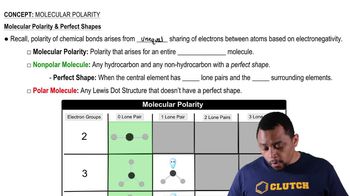
Molecular Polarity
Molecular polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charge across a molecule. It is determined by the shape of the molecule and the electronegativity differences between the atoms. A molecule is polar if it has a net dipole moment due to an uneven distribution of charge, while nonpolar molecules have symmetrical charge distributions.
Recommended video:
Molecular Polarity (Simplified) Concept 1
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. In polar molecules, there is a significant difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms, leading to partial positive and negative charges. In contrast, nonpolar molecules have atoms with similar electronegativities, resulting in an even sharing of electrons.
Recommended video:
Dipole Moment (Simplified) Concept 1
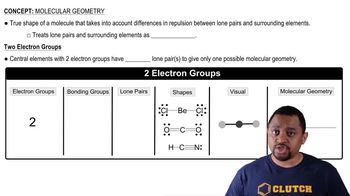
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. The shape influences the overall polarity; for example, CCl₄ has a tetrahedral shape that allows for symmetrical charge distribution, making it nonpolar. Conversely, PCl₃ has a trigonal pyramidal shape, leading to an uneven distribution of charge and making it polar.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry (Simplified) Concept 1