Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acid Side Chains
Amino acid side chains, or R groups, determine the chemical properties and functions of amino acids in proteins. They can be polar, nonpolar, acidic, or basic, influencing how they interact with substrates and other molecules. Understanding the nature of these side chains is crucial for predicting their roles in enzyme activity, including catalysis and substrate binding.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amino Acids Concept 1
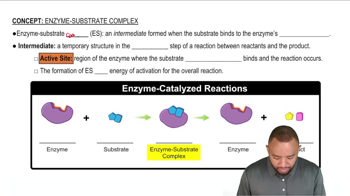
Enzyme Active Site
The active site of an enzyme is a specific region where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The structure and chemical environment of the active site are tailored to facilitate the conversion of substrates into products. The presence of specific amino acid side chains in this region can enhance catalytic efficiency or stabilize substrate binding.
Recommended video:
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Concept 1
Catalytic Function vs. Substrate Binding
Catalytic function refers to the ability of an enzyme to accelerate a chemical reaction, often involving specific amino acids that participate directly in the reaction mechanism. Substrate binding, on the other hand, involves interactions that hold the substrate in place for the reaction to occur. Some amino acids can fulfill both roles, making it essential to analyze their properties to determine their specific contributions.
Recommended video:
Enzyme-Substrate Complex Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution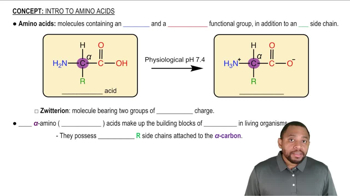


 2:32m
2:32m