Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. They follow the general formula CnH2n+2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are typically less reactive than other types of hydrocarbons and are commonly found in natural gas and petroleum.
Recommended video:
Alkenes
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons characterized by at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Their general formula is CnH2n, indicating that they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond, making them important in chemical synthesis and industrial applications.
Recommended video:
Cycloalkenes
Cycloalkenes are a subset of alkenes that contain a ring structure and at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They can be represented by the formula CnH2n-2, reflecting the ring's closure and the presence of the double bond. Cycloalkenes exhibit unique properties and reactivity due to their cyclic nature, making them significant in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Cyclic Alkanes Concept 1
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution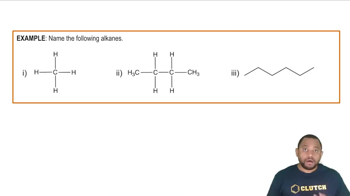



 4:29m
4:29m
