Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acid Properties
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. They have distinct properties based on their side chains, which can be polar, nonpolar, acidic, or basic. Leucine, alanine, glycine, and valine are classified as nonpolar or hydrophobic amino acids, meaning they tend to avoid water and are often found in the interior of proteins, contributing to the protein's overall structure.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
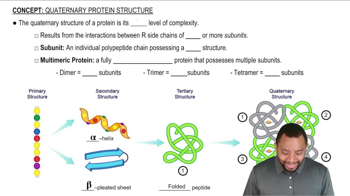
Protein Structure
Proteins have a complex structure that is organized into four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The arrangement of amino acids influences how a protein folds and its final shape. Nonpolar amino acids like leucine, alanine, glycine, and valine typically cluster in the interior of the protein, stabilizing its structure through hydrophobic interactions.
Recommended video:
Quaternary Protein Structure Concept 1
Hydrophobic Effect
The hydrophobic effect is a key principle in biochemistry that describes how nonpolar substances tend to aggregate in aqueous solutions to minimize their exposure to water. This phenomenon is crucial for protein folding, as it drives nonpolar amino acids to the interior of the protein, away from the surrounding water, thereby stabilizing the protein's three-dimensional structure.
Recommended video:
Solubility: Temperature Effect Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:16m
5:16m