Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas through the equation PV = nRT. In this context, it allows us to calculate the number of moles of HCl gas by using the given volume (15.0 L), pressure (1 atm), and temperature (25 °C).
Recommended video:
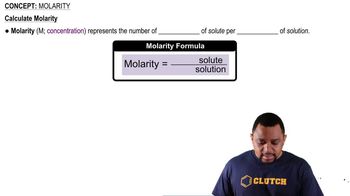
Molarity
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. In this problem, understanding molarity is essential for determining how the moles of HCl gas translate into a concentration when dissolved in 250.0 mL of water.
Recommended video:
Dissolution Process
The dissolution process refers to the interaction between solute and solvent that results in the solute becoming evenly distributed within the solvent. In this case, it is important to assume that all HCl gas dissolves in water, which simplifies the calculation of moles in solution without considering any losses or incomplete reactions.
Recommended video:
Processing of Pre-mRNA Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:15m
1:15m