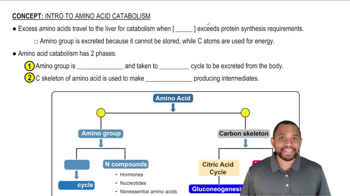
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Catabolism
Catabolism refers to the metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units, releasing energy in the process. This energy is often captured in the form of ATP, which can be used for various cellular functions. Catabolic processes include the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amino Acid Catabolism Concept 1
Anabolism
Anabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that construct molecules from smaller units, typically requiring energy input. This process is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells and tissues. Examples of anabolic processes include the synthesis of proteins from amino acids and the formation of nucleic acids from nucleotides.
Recommended video:
Intro to Metabolism Concept 1
Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Nucleic acid synthesis is the process by which cells create nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, from their building blocks, nucleotides. This process is crucial for genetic information storage and transmission. The synthesis of nucleic acids is an anabolic process, as it involves the assembly of smaller nucleotide units into larger, complex structures.
Recommended video:
Intro to Nucleic Acids Concept 1