Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Skeletal Structure of Organic Molecules
The skeletal structure, or line-angle structure, is a simplified way of representing organic molecules. In this format, carbon atoms are represented by the ends and intersections of lines, while hydrogen atoms are often omitted for clarity. This method allows chemists to visualize the molecular framework quickly, focusing on functional groups and overall shape.
Recommended video:
Skeletal Formula Concept 1
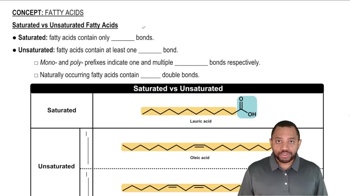
Saturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids are types of fatty acids that contain no double bonds between carbon atoms, meaning they are fully 'saturated' with hydrogen atoms. This structure typically results in a straight-chain configuration, allowing them to pack closely together, which contributes to their solid state at room temperature. Lauric acid, with its 12 carbon atoms, exemplifies this category.
Recommended video:
Lauric Acid
Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C12H24O2. It is primarily found in coconut oil and palm kernel oil and is known for its antimicrobial properties. In the context of nutrition, lauric acid is often discussed for its potential health benefits, including its role in raising HDL cholesterol levels.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution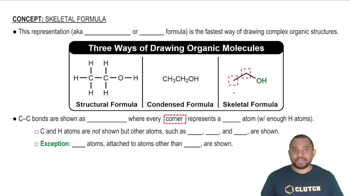


 2:0m
2:0m