Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Disubstituted Benzene
Disubstituted benzene refers to a benzene ring that has two substituents attached to it. The positions of these substituents can vary, leading to different isomers. Understanding the nomenclature and the implications of substituent positions is crucial for drawing accurate structural formulas.
Recommended video:
Disubstituted Benzene Example 2
Structural Formula
A structural formula represents the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how they are bonded together. It provides insight into the molecular structure, including the connectivity of atoms and the presence of functional groups. For disubstituted benzenes, it is important to depict the correct positions of the substituents on the benzene ring.
Recommended video:
Structural Formula Concept 2
Carbon Count in Organic Compounds
The total number of carbon atoms in a compound is essential for determining its molecular formula and structure. In this case, the requirement of 8 carbons means that the disubstituted benzene must be combined with additional carbon atoms, possibly in the form of alkyl groups. This understanding helps in constructing the correct structural formulas that meet the specified criteria.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution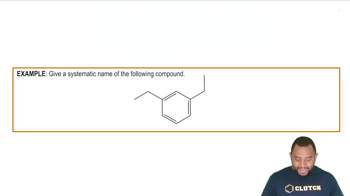



 :30m
:30m