Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acids
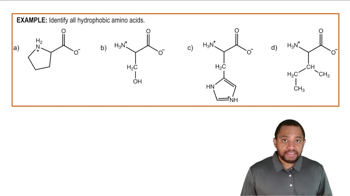
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that determines the specific properties of the amino acid. Understanding the structure of amino acids is essential for grasping how they link together to form proteins.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Isoleucine
Isoleucine (Ile) is one of the 20 standard amino acids and is classified as a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA). It has a non-polar side chain, which contributes to its hydrophobic nature. Isoleucine plays a crucial role in muscle metabolism and is important for energy production, making it vital for athletes and those engaged in physical training.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Classifications Example 1
Amino Acid Structure Representation
The structure of amino acids can be represented in various ways, including the Fischer projection and the ball-and-stick model. In a typical representation, the amino group (–NH2) is on one side, the carboxyl group (–COOH) on the opposite, and the side chain (R group) is attached to the central carbon. Understanding these representations is key to visualizing how amino acids interact and form proteins.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :41m
:41m