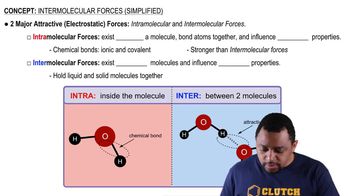
Textbook Question
Describe the formation of an aqueous KI solution, when solid KI dissolves in water.
465
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution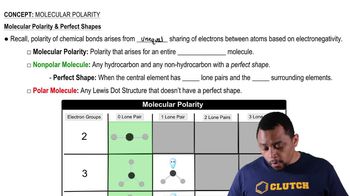


 2:35m
2:35mMaster Solubility and Intermolecular Forces Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules Bruno
Start learning