Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Elimination Reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of chemical reaction where a molecule loses atoms or groups of atoms, resulting in the formation of a double bond or a ring structure. In the case of converting bromocyclohexane to cyclohexene, the reaction involves the removal of a bromine atom and a hydrogen atom, leading to the formation of a carbon-carbon double bond.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions Dehydration Reactions Example 1
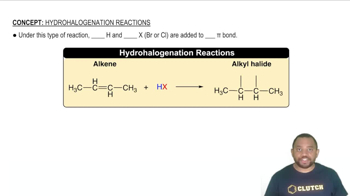
Dehydrohalogenation
Dehydrohalogenation is a specific type of elimination reaction where a hydrogen halide (like HBr) is removed from a haloalkane. This process is crucial in the conversion of bromocyclohexane to cyclohexene, as it involves the elimination of bromine and a hydrogen atom, resulting in the formation of an alkene.
Recommended video:
Hydrohalogenation Reaction Concept 1
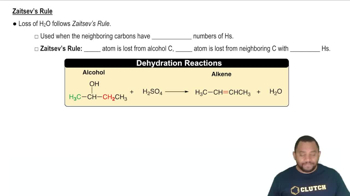
Zaitsev's Rule
Zaitsev's Rule states that in elimination reactions, the more substituted alkene is typically the major product. This principle helps predict the outcome of the reaction when converting bromocyclohexane to cyclohexene, as the stability of the resulting alkene can influence the reaction pathway and product distribution.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution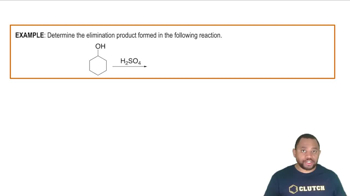

 1:11m
1:11m