Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
NADH
NADH stands for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (in its reduced form). It is a coenzyme found in all living cells and plays a crucial role in metabolic processes, particularly in cellular respiration. NADH is involved in the transfer of electrons in the electron transport chain, which is essential for ATP production.
Recommended video:
Total Energy From Glucose Example 1
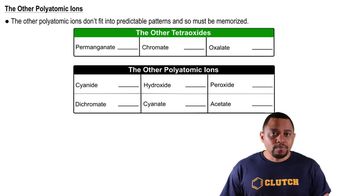
H⁺ Ion
H⁺ refers to a hydrogen ion, which is a proton that has lost its electron. In biochemical contexts, H⁺ ions are important for maintaining pH balance and are involved in various metabolic reactions. The concentration of H⁺ ions can influence enzyme activity and is critical in processes like ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis.
Recommended video:
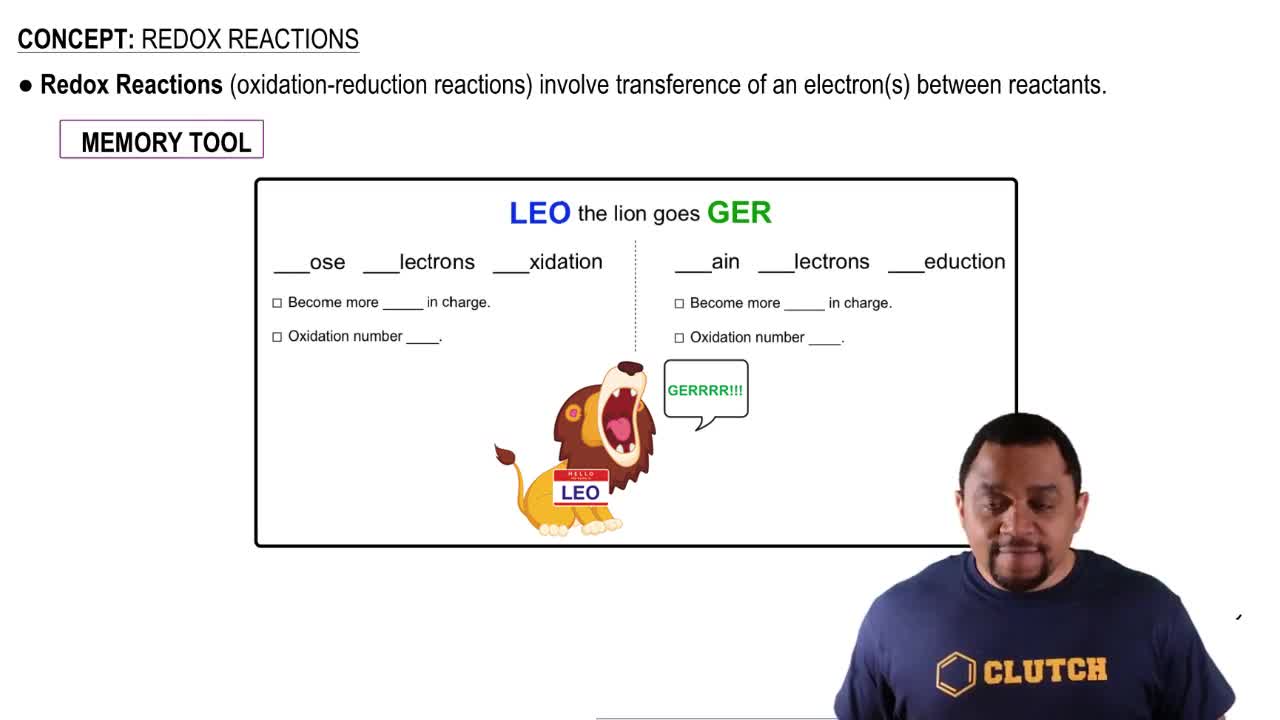
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions, short for reduction-oxidation reactions, are chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons between two species. In the context of NADH and H⁺, NADH acts as an electron donor (reducing agent), while H⁺ ions can accept electrons (oxidizing agent). These reactions are fundamental to energy production in cells, particularly during cellular respiration.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 2:23m
2:23m