Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Structure
Molecular structure refers to the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, including the types of bonds and the spatial orientation of the atoms. In H₂S, the central sulfur (S) atom is bonded to two hydrogen (H) atoms, which influences the molecule's shape and properties. Understanding molecular structure is essential for predicting how molecules interact and behave in different environments.
Recommended video:
Molecular Models Example 1
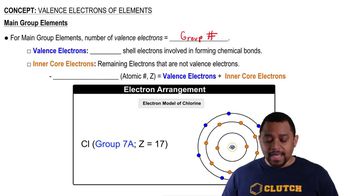
Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that are involved in forming bonds with other atoms. Sulfur has six valence electrons, and in H₂S, it shares two of these with two hydrogen atoms, allowing for the formation of two covalent bonds. This concept is crucial for understanding how many atoms can bond to a central atom and the resulting molecular geometry.
Recommended video:
Valence Electrons of Elements (Simplified) Concept 1
Coordination Number
Coordination number refers to the number of atoms, ions, or molecules that are bonded to a central atom in a complex or molecule. In the case of H₂S, the coordination number of the sulfur atom is two, as it is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This concept helps in understanding the bonding capacity of an atom and its implications for molecular shape and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Calculate Oxidation Numbers
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:25m
2:25m