Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Strong Electrolytes
Strong electrolytes are substances that completely dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. This means that in an aqueous solution, they exist solely as ions, which can conduct electricity. Common examples include salts like sodium bromide (NaBr), which, when dissolved, separates into Na+ and Br- ions.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes (Simplified) Concept 1
Dissociation in Aqueous Solutions
Dissociation refers to the process by which an ionic compound separates into its constituent ions in a solvent, typically water. In the case of NaBr, the ionic bonds between sodium and bromide ions break, allowing them to disperse throughout the solution as free-moving ions, which is essential for understanding the behavior of electrolytes in solution.
Recommended video:
Ionic vs. Molecular Compounds
Ionic compounds, like NaBr, consist of charged ions held together by electrostatic forces, while molecular compounds are formed by covalent bonds between atoms. In aqueous solutions, ionic compounds typically yield only ions, whereas molecular compounds may remain as whole molecules or partially dissociate, affecting their conductivity and chemical behavior in solution.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution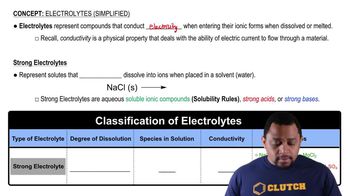



 2:38m
2:38m