Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Reduction Reaction
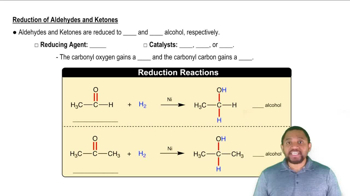
A reduction reaction involves the gain of electrons or hydrogen by a molecule, resulting in a decrease in oxidation state. In organic chemistry, this often refers to the conversion of carbonyl compounds, like ketones, into alcohols. The process typically requires a reducing agent, such as hydrogen gas, and a catalyst, like nickel, to facilitate the reaction.
Recommended video:
Reduction Reactions Concept 1
Condensed Structural Formula
A condensed structural formula is a way of representing a chemical compound that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule without depicting all the bonds explicitly. It provides a simplified view of the molecular structure, indicating how atoms are grouped together. For example, in alcohols, the hydroxyl (-OH) group is highlighted, showing its connection to the carbon chain.
Recommended video:
Condensed Formula Concept 1
Nickel Catalyst
A nickel catalyst is a substance that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. In the context of hydrogenation reactions, nickel is commonly used to facilitate the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated compounds, such as ketones. Its role is crucial in ensuring that the reduction occurs efficiently, leading to the formation of the desired alcohol.
Recommended video:
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution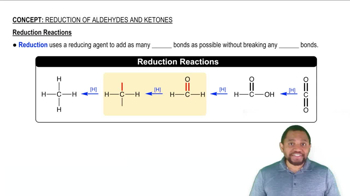


 2:38m
2:38m