Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ethanol Oxidation
Ethanol oxidation is a chemical process where ethanol (C2H5OH) is converted into acetic acid (CH3COOH) through the action of microorganisms, typically acetic acid bacteria. This process involves the conversion of ethanol to acetaldehyde and then to acetic acid, which is the primary component of vinegar. Understanding this transformation is crucial for grasping how designer vinegars are produced from various wines.
Recommended video:
Oxidation of Monosaccharides Concept 1
Acetic Acid Structure
Acetic acid, the main component of vinegar, has the chemical formula CH3COOH. Its structure consists of a methyl group (CH3) attached to a carboxyl group (COOH). This simple structure is responsible for the characteristic sour taste of vinegar and its use in culinary applications. Recognizing the molecular structure of acetic acid is essential for understanding its properties and reactions.
Recommended video:
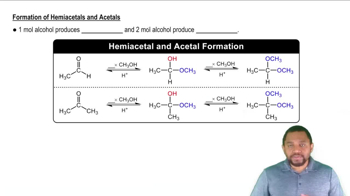
Formation of Hemiacetals and Acetals Concept 2
Microbial Fermentation
Microbial fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms, such as bacteria and yeast, convert sugars and other substrates into acids, gases, or alcohol. In the case of vinegar production, acetic acid bacteria play a key role in fermenting ethanol into acetic acid. This concept is vital for understanding how different types of vinegars are created and the role of microorganisms in food production.
Recommended video:
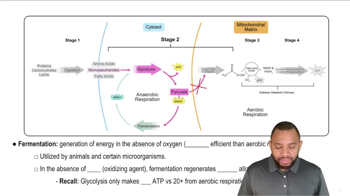
Anaerobic Respiration Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution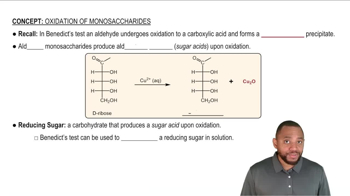

 1:49m
1:49m