Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ester Hydrolysis
Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where an ester reacts with water to form an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. This process can occur under acidic or basic conditions, but in this case, we focus on acid hydrolysis, which involves the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction is important in organic chemistry as it helps in understanding the behavior of esters in various environments.
Recommended video:
Acid-Catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis Concept 1
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction with equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. Balancing is crucial because it reflects the law of conservation of mass, ensuring that matter is neither created nor destroyed during the reaction. In the case of methyl butanoate hydrolysis, the equation must accurately depict the reactants and products involved.
Recommended video:
Balancing Chemical Equations (Simplified) Concept 1
Acid Catalysis
Acid catalysis involves the use of an acid to increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. In the context of ester hydrolysis, the acid donates protons to the ester, facilitating the breakdown of the ester bond. This concept is essential for understanding how the reaction proceeds more efficiently under acidic conditions compared to neutral or basic environments.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution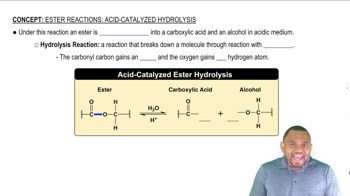


 1:14m
1:14m