Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
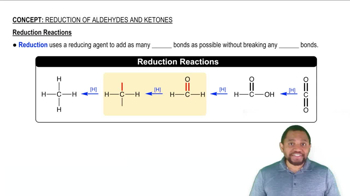
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
Oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions are chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons between substances. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons. These reactions are fundamental in biological systems, particularly in energy production, where they facilitate the conversion of energy stored in nutrients into usable forms.
Recommended video:
Reduction Reactions Concept 1
Iron Ions in Biological Systems
Iron ions, particularly in the forms of Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺, play a crucial role in biological systems, especially in electron transport chains. In these systems, iron-containing proteins, such as cytochromes, facilitate electron transfer, which is essential for ATP production in mitochondria. The interconversion between Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺ is a key aspect of redox reactions in cellular respiration.
Recommended video:
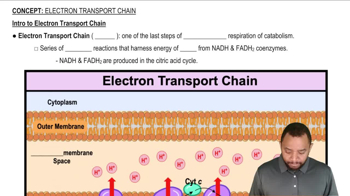
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons derived from nutrients. As electrons move through the chain, they release energy used to pump protons across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient drives ATP synthesis, making the ETC a vital component of aerobic respiration and energy production in cells.
Recommended video:
Intro to Electron Transport Chain Concept 1