Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation of Alcohols
Oxidation of alcohols involves the conversion of alcohol functional groups into carbonyl groups. In the case of primary alcohols, such as 3-chloro-1-propanol, oxidation typically leads to the formation of aldehydes. This process can be facilitated by oxidizing agents like potassium dichromate or PCC, which remove hydrogen atoms from the alcohol.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Oxidation Concept 1
Condensed Structural Formulas
Condensed structural formulas provide a simplified representation of a molecule's structure, showing the arrangement of atoms without depicting all the bonds explicitly. For example, the condensed formula for an aldehyde derived from 3-chloro-1-propanol would highlight the carbonyl group (C=O) and the attached hydrogen atom, indicating its functional group characteristics.
Recommended video:
Condensed Formula Concept 1
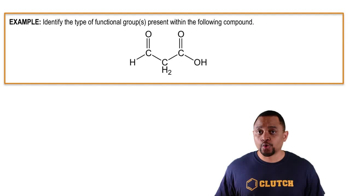
Functional Groups: Aldehydes and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes and carboxylic acids are important functional groups in organic chemistry. Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom, while carboxylic acids have a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the same carbon. Understanding these functional groups is essential for predicting the products of oxidation reactions involving alcohols.
Recommended video:
Functional Groups with Carbonyls Example 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution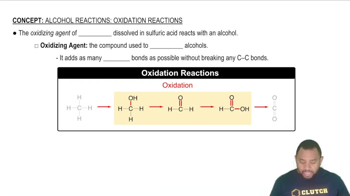


 1:49m
1:49m