Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Weak Base
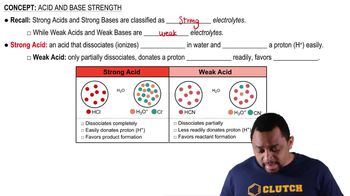
A weak base is a substance that partially ionizes in solution, meaning it does not completely dissociate into its ions. In the case of ammonia (NH₃), it reacts with water to form ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻), but only a fraction of the ammonia molecules undergo this reaction. This characteristic leads to a lower pH compared to strong bases.
Recommended video:
Acid and Base Strength Concept 4
Dissociation in Water
Dissociation in water refers to the process by which a compound separates into its constituent ions when dissolved. For weak bases like NH₃, this process is incomplete, resulting in an equilibrium between the undissociated base and the ions produced. Understanding this equilibrium is crucial for predicting the behavior of weak bases in aqueous solutions.
Recommended video:
Acid and Base Strength Concept 1
pH and Basicity
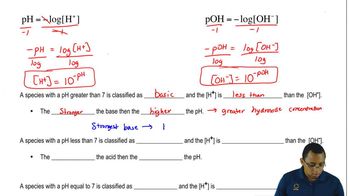
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, with lower values indicating acidity and higher values indicating basicity. When NH₃ dissolves in water, it increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, which raises the pH of the solution, making it basic. The extent of this increase depends on the concentration of the weak base and its degree of ionization.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 3:17m
3:17m