Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coenzymes
Coenzymes are organic molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing reactions. They often act as carriers for chemical groups or electrons during metabolic processes. In the context of biochemical reactions, coenzymes are crucial for facilitating the transfer of atoms or functional groups, thereby enhancing the efficiency of enzymatic activity.
Recommended video:
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the addition of hydrogen (H2) to a compound, typically an unsaturated organic molecule. This process often converts carbon–carbon double bonds into single bonds, resulting in saturated compounds. Understanding hydrogenation is essential for grasping how certain coenzymes function in metabolic pathways, particularly in the context of fatty acid synthesis.
Recommended video:
Hydrogenation Reactions Concept 1
NADH
NADH (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a key coenzyme in cellular metabolism that plays a vital role in redox reactions. It acts as an electron carrier, picking up hydrogen ions and electrons during metabolic processes. In the formation of carbon–carbon double bonds, NADH is often involved in the reduction reactions that convert unsaturated compounds into saturated ones, highlighting its importance in biochemical pathways.
Recommended video:
Total Energy From Glucose Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution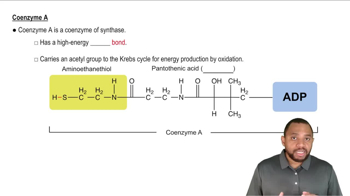



 2:2m
2:2m