Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ammonia Toxicity
Ammonia (NH₃) is a byproduct of protein metabolism and is highly toxic to cells. In mammals, the accumulation of ammonia can lead to severe neurological damage and other health issues. Therefore, the body must convert ammonia into less toxic forms for safe excretion.
Recommended video:
Acid-Base Reaction Example 1
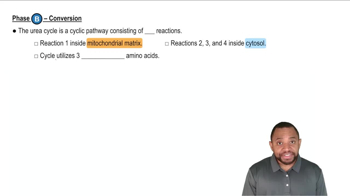
Urea Cycle
The urea cycle is a series of biochemical reactions that convert ammonia into urea, which is far less toxic. This cycle occurs primarily in the liver and involves several enzymes that facilitate the transformation of ammonia into urea, allowing for its safe transport and excretion through urine.
Recommended video:
Nitrogen Excretion
Nitrogen excretion is a crucial physiological process for removing excess nitrogen from the body, primarily derived from amino acid metabolism. Urea is the main nitrogenous waste product in mammals, as it is water-soluble and can be efficiently excreted by the kidneys, thus maintaining nitrogen balance and preventing toxicity.
Recommended video:
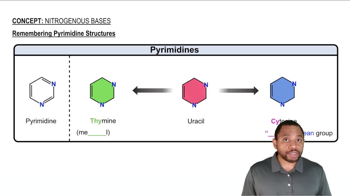
Nitrogenous Bases Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:31m
1:31m