Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a crucial coenzyme found in all living cells. It plays a vital role in metabolic processes, particularly in redox reactions, where it alternates between oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) forms. NAD is derived from niacin (vitamin B3), which is essential for its synthesis, linking it directly to the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Recommended video:
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Concept 2
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, is a water-soluble vitamin that is important for energy metabolism and the synthesis of NAD and NADP. It exists in two forms: nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. Niacin is essential for converting food into energy and maintaining healthy skin, nerves, and digestive systems, highlighting its significance in overall metabolic health.
Recommended video:
Metabolic Pathways
Metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell that convert substrates into products, facilitating energy production and biosynthesis. These pathways are interconnected and regulated, allowing cells to respond to changes in their environment. Understanding these pathways is crucial for comprehending how nutrients, including nucleotides like NAD, are utilized in cellular metabolism.
Recommended video:
Metabolic Pathways Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution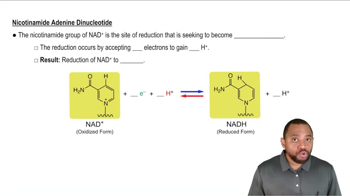



 2:39m
2:39m