Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the metabolic process by which cells convert nutrients into energy, specifically ATP. It involves glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Understanding this process is crucial for determining how different molecules, like glucose and maltose, are broken down to produce ATP.
Recommended video:
Anaerobic Respiration Concept 1
ATP Yield from Carbohydrates
Different carbohydrates yield varying amounts of ATP upon metabolism. For instance, glucose typically produces about 30-32 ATP molecules per mole, while maltose, a disaccharide, is broken down into two glucose units, potentially yielding a similar amount. Recognizing these differences is essential for comparing their energy outputs.
Recommended video:
Molecular Structure and Energy Content
The molecular structure of carbohydrates affects their energy content and how efficiently they can be metabolized. Glucose, a monosaccharide, is more readily utilized in cellular respiration compared to maltose, which requires additional enzymatic steps for breakdown. This structural difference influences the total ATP produced from each molecule.
Recommended video:
Molecular Models Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution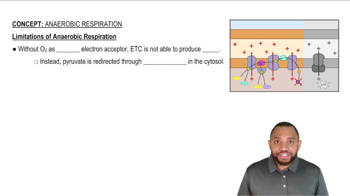



 1:49m
1:49m