Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
β-Oxidation
β-Oxidation is a metabolic process that breaks down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA units, which can then enter the citric acid cycle for energy production. This process occurs in the mitochondria and involves the sequential removal of two-carbon units from the fatty acid chain, starting from the carboxyl end.
Recommended video:
Oxidation of Monosaccharides Concept 1
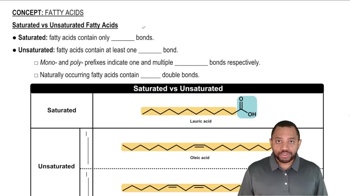
Saturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids, like lauric acid, contain no double bonds between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon chain. This structure allows them to pack closely together, resulting in a solid state at room temperature. The number of carbon atoms in a saturated fatty acid influences the number of β-oxidation cycles it undergoes.
Recommended video:
Cycle Calculation
The number of β-oxidation cycles for a fatty acid can be calculated using the formula: (n/2) - 1, where n is the total number of carbon atoms in the fatty acid. Each cycle shortens the fatty acid chain by two carbon atoms, producing one acetyl-CoA molecule per cycle until the entire chain is converted.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution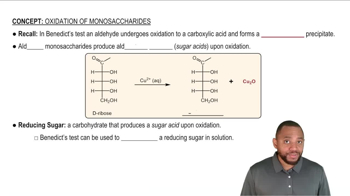

 1:29m
1:29m