Textbook Question
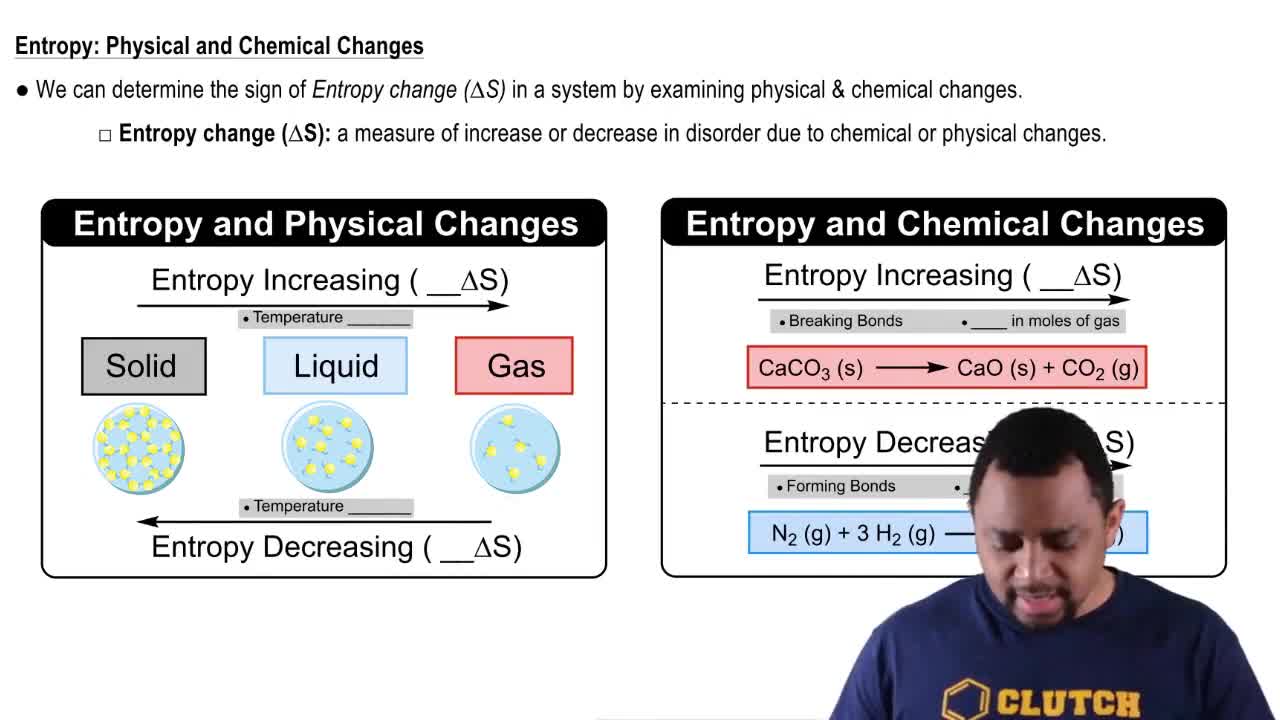
Does entropy increase or decrease in the following processes?
2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
279
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 0:54m
0:54mMaster Entropy (Simplified) Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules Bruno
Start learning