Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dissociation of Acids
Dissociation refers to the process by which an acid separates into its constituent ions in solution. In the case of trichloroacetic acid, it partially dissociates into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and trichloroacetate ions (CCl₃CO₂⁻). Understanding the extent of dissociation is crucial for calculating the concentration of ions in solution, which directly affects properties like freezing point.
Recommended video:
Acid and Base Strength Concept 1
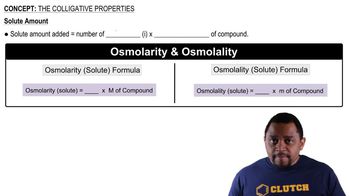
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles rather than their identity. Freezing point depression is one such property, where the presence of solute particles lowers the freezing point of a solvent. The formula for calculating the change in freezing point involves the van 't Hoff factor, which accounts for the number of particles produced from the solute's dissociation.
Recommended video:
The Colligative Properties Concept 3
Freezing Point Depression
Freezing point depression quantifies how much the freezing point of a solvent decreases when a solute is added. For every mole of solute particles, the freezing point of water decreases by 1.86 °C. In this scenario, knowing the percentage of dissociation allows us to determine the effective number of solute particles, which is essential for calculating the new freezing point of the solution.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution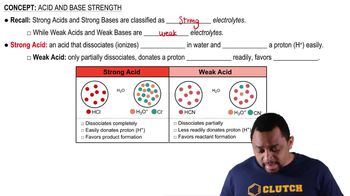


 2:m
2:m