Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). It is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in a chemical formula. Understanding molar mass is essential for converting between grams and moles, which is a fundamental concept in stoichiometry and chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula represents the composition of a compound, indicating the types and numbers of atoms present. For example, C₃H₆O₃ indicates that the compound contains three carbon (C) atoms, six hydrogen (H) atoms, and three oxygen (O) atoms. Recognizing how to interpret chemical formulas is crucial for calculating molar mass and understanding the structure of compounds.
Recommended video:
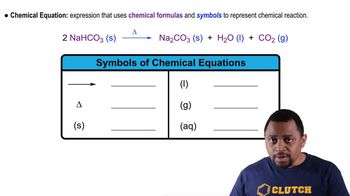
Chemical Reaction: Chemical Change Concept 2
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of an element's isotopes, measured in atomic mass units (amu). Each element has a specific atomic mass that contributes to the overall molar mass of a compound. Familiarity with atomic masses from the periodic table is necessary for accurately calculating the molar mass of compounds like C₃H₆O₃.
Recommended video:
Atomic Mass (Conceptual) Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:10m
1:10m