Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a series of enzymatic reactions that occur in the mitochondria. It plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by oxidizing acetyl-CoA to produce energy carriers, including NADH and FADH2, which are essential for ATP production in the electron transport chain.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
FADH2 Production
FADH2 is a reduced form of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and serves as an important electron carrier in the citric acid cycle. It is produced during specific reactions, such as the conversion of succinate to fumarate, where FAD is reduced to FADH2, capturing energy that can later be used to generate ATP.
Recommended video:
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) Concept 2
Energy Transfer in Metabolism
Energy transfer in metabolism refers to the process by which energy is captured and stored in the form of high-energy molecules like ATP, NADH, and FADH2. In the context of the citric acid cycle, the transfer of energy as FADH2 is vital for the subsequent production of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, highlighting the interconnectedness of metabolic pathways.
Recommended video:
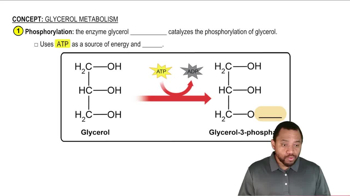
Glycerol Metabolism Concept 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution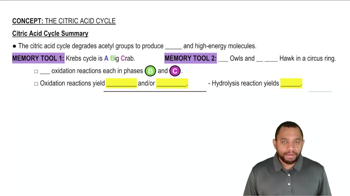


 :50m
:50m