Textbook Question
Are polynucleotides synthesized 3′ to 5′ or 5′ to 3′?
953
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

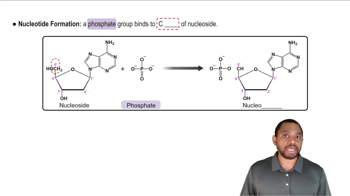
Are polynucleotides synthesized 3′ to 5′ or 5′ to 3′?
Draw the complete structure of uridine 5′- phosphate, one of the four major ribonucleotides.
Draw the complete structure of the RNA dinucleotide U-C. Identify the 5′ and 3′ ends of the dinucleotide.
What does it mean to speak of bases as being complementary?
The DNA from sea urchins contains about 32% A and about 18% G. What percentages of T and C would you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.