Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy. It takes place in the mitochondria and involves the oxidation of acetyl-CoA to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH2, which are crucial for cellular respiration. Understanding this cycle is essential for identifying specific reactions and their roles in energy production.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
GTP Formation
GTP (guanosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide similar to ATP and serves as an energy currency in the cell. In the citric acid cycle, GTP is produced through substrate-level phosphorylation, specifically during the conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinate. Recognizing the conditions and enzymes involved in GTP formation is vital for answering questions related to energy metabolism.
Recommended video:
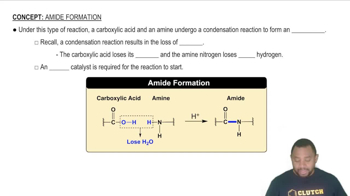
Amide Formation Concept 1
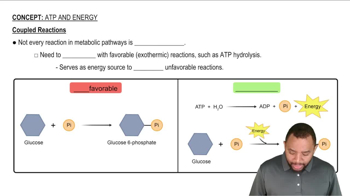
Coupled Reactions
Coupled reactions occur when an energetically unfavorable reaction is driven by an energetically favorable one, allowing the overall process to proceed. In the context of the citric acid cycle, the reaction that produces GTP is coupled with the hydrolysis of succinyl-CoA, which releases energy. Understanding this coupling is important for grasping how energy is efficiently transferred and utilized in metabolic pathways.
Recommended video:
Coupled Reactions Concept 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution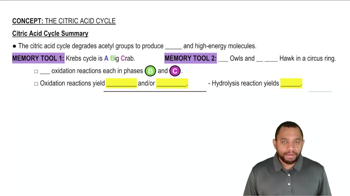

 :50m
:50m