Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Substrate
A substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. In biochemical reactions, substrates bind to the active site of enzymes, facilitating the conversion of substrates into products. For example, glucose serves as a substrate for various enzymes involved in metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis.
Recommended video:
Enzyme-Substrate Complex Concept 1
Enzyme
An enzyme is a biological catalyst that accelerates chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes are typically proteins that lower the activation energy required for reactions, allowing them to occur more efficiently. Each enzyme is specific to a particular substrate, which determines its function in metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Intro to Enzymes Concept 1
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
The enzyme-substrate complex is a temporary molecular structure formed when a substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme. This complex is crucial for the catalytic activity of the enzyme, as it stabilizes the transition state and facilitates the conversion of substrates into products. Understanding this interaction is key to grasping how enzymes function in biochemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Enzyme-Substrate Complex Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution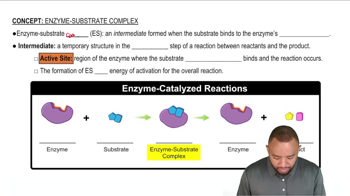



 :39m
:39m