Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cofactors
Cofactors are non-protein chemical compounds that assist enzymes in catalyzing reactions. They can be metal ions, such as zinc or magnesium, or organic molecules. Cofactors are essential for the biological activity of many enzymes, as they help stabilize enzyme-substrate complexes or participate directly in the chemical reaction.
Recommended video:
Intro to Cofactors Concept 1
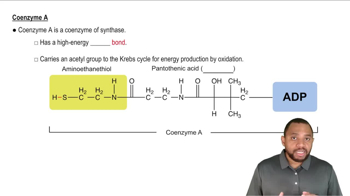
Coenzymes
Coenzymes are a specific type of cofactor that are organic molecules, often derived from vitamins. They bind to enzymes and assist in the transfer of specific functional groups during biochemical reactions. Unlike cofactors, coenzymes are often altered during the reaction and need to be regenerated for further use, making them crucial for metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Pyridoxyl Phosphate
Pyridoxyl phosphate is the active form of vitamin B6 and serves as a coenzyme in various enzymatic reactions, particularly those involving amino acid metabolism. It plays a critical role in transamination, decarboxylation, and other reactions, facilitating the transfer of amino groups. Understanding its function helps distinguish it as a coenzyme rather than a simple cofactor.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:23m
2:23m