Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Addition Reactions
Addition reactions involve the combination of two or more reactants to form a single product. In these reactions, unsaturated compounds, such as alkenes or alkynes, react with other molecules, resulting in the formation of new bonds. A common example is the reaction of ethylene (H₂C═CH₂) with hydrogen chloride (HCl), which produces chloroethane (CH₃CH₂Cl).
Recommended video:
Addition Reactions Concept 1
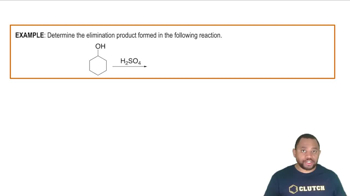
Elimination Reactions
Elimination reactions occur when a single reactant breaks down into two products, typically involving the removal of a small molecule like water or hydrogen halide. These reactions often convert saturated compounds into unsaturated ones. For instance, the reaction of bromoethane (CH₃CH₂Br) to form ethylene (H₂C═CH₂) and hydrogen bromide (HBr) is a classic example of an elimination reaction.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions Dehydration Reactions Example 1
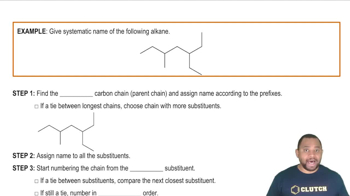
Substitution Reactions
Substitution reactions involve the replacement of one atom or group in a molecule with another atom or group. This type of reaction is common in organic chemistry, particularly with alkyl halides. An example is the reaction of methyl bromide (CH₃Br) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), where the bromine atom is replaced by a hydroxyl group, resulting in methanol (CH₃OH) and sodium bromide (NaBr).
Recommended video:
Naming Alkanes with Substituents Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution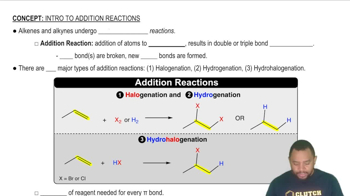

 2:55m
2:55m