Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
NADH and NAD⁺ Role in Metabolism
NADH and NAD⁺ are crucial coenzymes in cellular metabolism, particularly in redox reactions. NADH acts as an electron carrier, facilitating the transfer of electrons during metabolic processes. The conversion of NADH back to NAD⁺ is essential for maintaining the balance of these coenzymes, which is vital for ongoing metabolic reactions, especially in anaerobic conditions.
Recommended video:
Glycerol Metabolism Concept 2
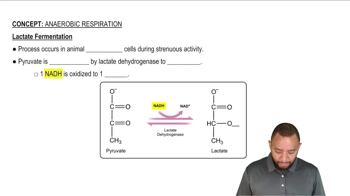
Lactate Fermentation
Lactate fermentation is an anaerobic process where pyruvate is converted to lactate, allowing glycolysis to continue in the absence of oxygen. This process regenerates NAD⁺ from NADH, enabling glycolysis to produce ATP, which is crucial for energy production in cells under low-oxygen conditions. Without this regeneration, glycolysis would halt, leading to energy depletion.
Recommended video:
Anaerobic Respiration Concept 3
Cellular Energy Production
Cellular energy production primarily occurs through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. In situations where oxygen is limited, cells rely on anaerobic pathways like lactate fermentation to generate ATP. The conversion of NADH to NAD⁺ during lactate fermentation is vital for sustaining ATP production, ensuring that cells can continue to function even in anaerobic environments.
Recommended video:
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Example 1