Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lactase
Lactase is the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose into its constituent monosaccharides, glucose and galactose, which can then be absorbed by the body. Individuals who lack sufficient lactase may experience lactose intolerance, leading to digestive issues when consuming dairy.
Recommended video:
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Example 2
Enzyme Function
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body without being consumed in the process. They work by lowering the activation energy required for reactions, allowing substrates to convert into products more efficiently. Each enzyme is specific to a particular substrate, which is determined by the enzyme's active site structure.
Recommended video:
Substrate Specificity
Substrate specificity refers to the ability of an enzyme to selectively bind to a particular substrate and catalyze a specific reaction. This specificity is crucial for metabolic pathways, as it ensures that enzymes only act on the intended molecules, preventing unwanted reactions. The unique shape and chemical properties of the enzyme's active site determine this specificity.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution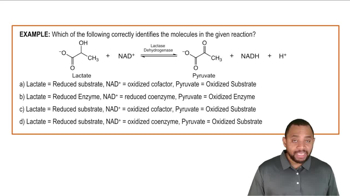



 :39m
:39m