Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce on its own, requiring them to be obtained through diet. They are crucial for various bodily functions, including heart health and brain development. The primary types include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), with EPA and DHA primarily sourced from fatty fish.
Recommended video:
Skeletal Structures of Fatty Acids
The skeletal structure of fatty acids represents their molecular framework, illustrating the arrangement of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. For EPA and DHA, these structures highlight the number of carbon atoms and the presence of double bonds, which are critical for understanding their chemical properties and biological functions. Drawing these structures helps visualize the differences between various fatty acids.
Recommended video:
Role of DHA in Brain Development
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a vital omega-3 fatty acid that plays a significant role in brain development and function. It is particularly important during infancy, as it contributes to the growth of neural tissues and cognitive development. DHA is abundant in breast milk and is often added to infant formulas to ensure adequate intake for optimal brain health.
Recommended video:
Gluconeogenesis Concept 8
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution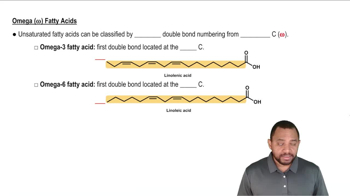


 2:0m
2:0m