Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Anabolic Pathways
Anabolic pathways are metabolic processes that build larger molecules from smaller ones, requiring energy input. These pathways are essential for growth, repair, and the synthesis of complex biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides. An example of an anabolic process is protein synthesis, where amino acids are linked together to form proteins.
Recommended video:
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Concept 1
Catabolic Pathways
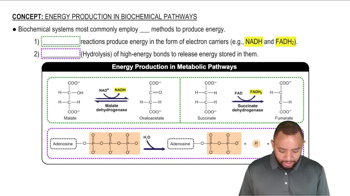
Catabolic pathways are metabolic processes that break down larger molecules into smaller units, releasing energy in the process. This energy is often captured in the form of ATP, which cells use for various functions. An example of a catabolic pathway is glycolysis, where glucose is broken down to produce energy.
Recommended video:
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Concept 1
Citric Acid Cycle
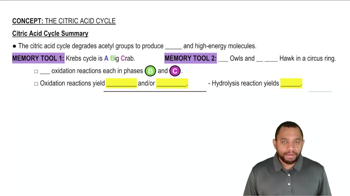
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a key metabolic pathway that plays a central role in cellular respiration. It is primarily catabolic, as it involves the breakdown of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to produce energy carriers like NADH and FADH2. These carriers then feed into the electron transport chain to generate ATP.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12