Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed through the electrostatic attraction between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). They typically consist of a metal and a non-metal, resulting in a crystalline structure with high melting and boiling points. Common examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and magnesium oxide (MgO).
Recommended video:
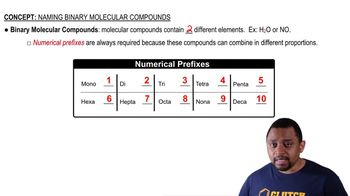
Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more non-metals share electrons through covalent bonds. These compounds can exist as discrete molecules and often have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds. Water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) are classic examples of molecular compounds.
Recommended video:
Naming Binary Molecular Compounds Concept 1
Naming Conventions
The naming of chemical compounds follows specific conventions based on their structure and composition. Ionic compounds are named by combining the names of the cation and anion, while molecular compounds use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms present. For example, Cl₂O₇ is named dichlorine heptoxide, reflecting its molecular nature and the number of chlorine and oxygen atoms.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Thiols Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:10m
1:10m