Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes are a class of hydrocarbons characterized by a ring structure composed of carbon atoms. They are saturated compounds, meaning they contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. The simplest cycloalkane is cyclopropane, which consists of three carbon atoms in a triangular formation. Understanding cycloalkanes is essential for identifying their properties and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Rules for Naming Cyclic Alkanes Concept 1
Substituents
Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms that replace hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon structure. In the context of cycloalkanes, substituents can be various functional groups or other hydrocarbons that modify the properties of the base compound. The presence and arrangement of substituents significantly influence the chemical behavior and physical properties of the cycloalkane.
Recommended video:
Naming Alkanes with Substituents Example 1
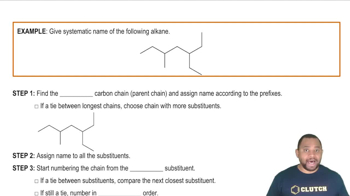
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Nomenclature refers to the systematic naming of chemical compounds based on established rules. For cycloalkanes with substituents, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides guidelines for naming, which include identifying the main cycloalkane structure and numbering the carbon atoms to give the substituents the lowest possible numbers. This understanding is crucial for accurately communicating the structure of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:26m
2:26m