Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Representative Elements
Representative elements are found in groups 1, 2, and 13-18 of the periodic table. They are characterized by their ability to form a wide variety of compounds and exhibit predictable properties based on their group. Understanding these elements is crucial for predicting the behavior of ionic compounds, such as XCl₃, where X represents a representative element.
Recommended video:
Periodic Table: Representative Elements & Transition Metals
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when atoms transfer electrons, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. In the case of XCl₃, X is a cation derived from the representative element, while Cl is a chloride anion. The ratio of these ions in the compound reflects the charges of the ions, which is essential for determining the group number of X.
Recommended video:
Periodic Table Group Number
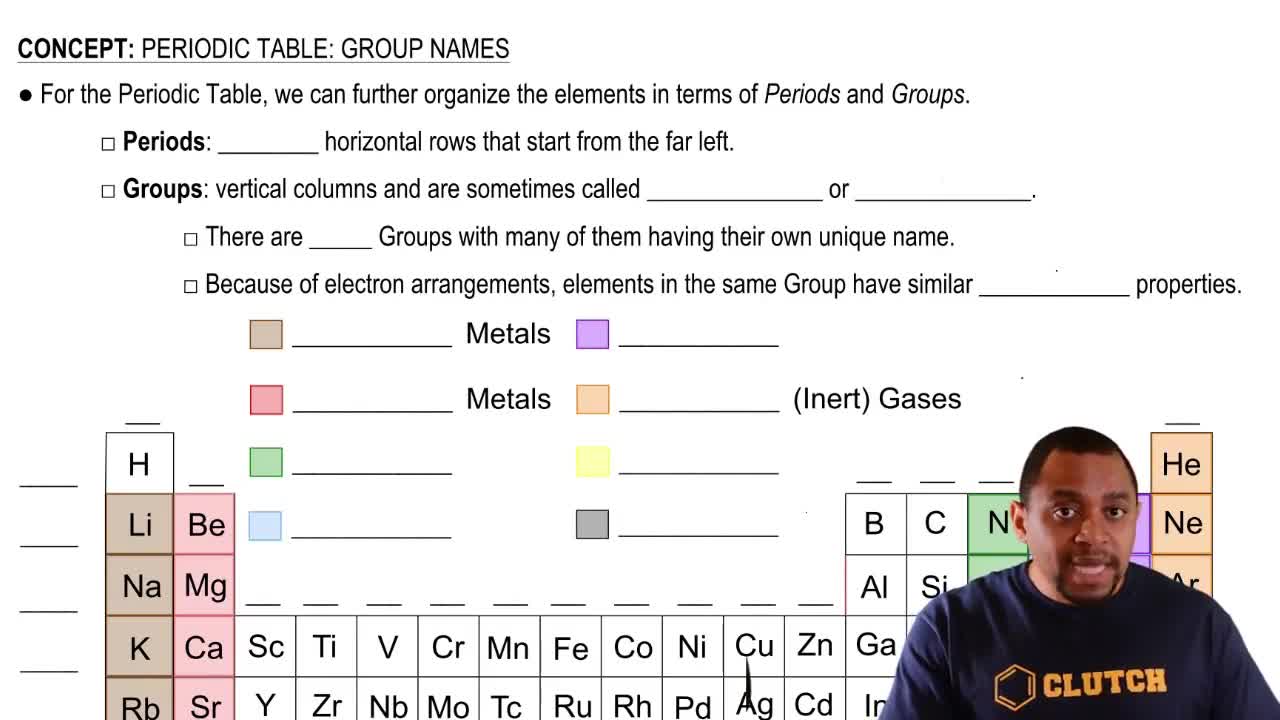
The group number in the periodic table indicates the number of valence electrons in the outer shell of an element. For representative elements, this directly influences their ionic charge when forming compounds. By analyzing the ionic compound XCl₃, one can deduce the group number of X based on the charge of the chloride ion (Cl⁻) and the overall neutrality of the compound.
Recommended video:
Periodic Table: Group Names
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution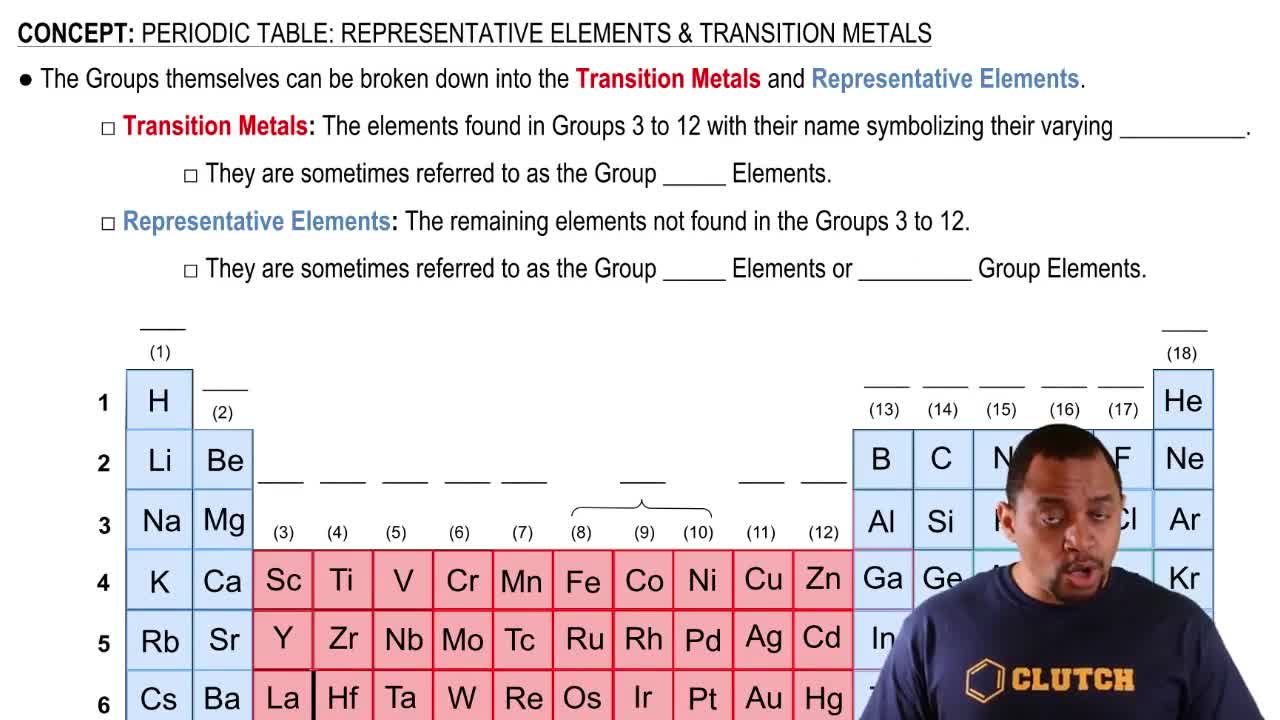


 2:33m
2:33m