Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dehydration Reaction
A dehydration reaction is a chemical process where a water molecule is removed from a compound, typically resulting in the formation of a double bond. In organic chemistry, this often involves the conversion of alcohols into alkenes. Understanding this reaction is crucial for predicting the products formed when an alcohol undergoes dehydration.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Alcohol Structure
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. The structure of the alcohol significantly influences the outcome of the dehydration reaction, as the position of the hydroxyl group and the carbon skeleton determine the major alkene product formed. Identifying the correct alcohol structure is essential for synthesizing the desired alkene.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Classification Concept 2
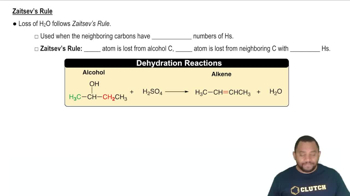
Zaitsev's Rule
Zaitsev's Rule states that in elimination reactions, the more substituted alkene is typically the major product. This principle helps predict which alkene will be favored during the dehydration of alcohols. Understanding this rule is important for determining the structure of the alcohol that will yield the specified alkene as the major product.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:3m
1:3m