Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Biological Transformations
Biological transformations refer to the chemical reactions that occur within living organisms, enabling them to convert substrates into products. These transformations are essential for metabolism, growth, and energy production. They can be categorized into three main types: additions, eliminations, and substitutions, which describe how molecular structures change during these reactions.
Recommended video:
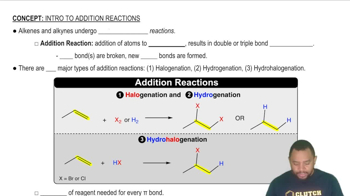
Addition Reactions
Addition reactions involve the combination of two or more molecules to form a single product. In biological systems, these reactions often occur in metabolic pathways where functional groups are added to substrates, enhancing their reactivity or facilitating further transformations. An example is the conversion of fumaric acid to malic acid, where a water molecule is added to the double bond of fumaric acid.
Recommended video:
Addition Reactions Concept 1
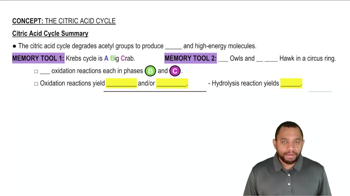
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a crucial metabolic pathway that takes place in the mitochondria of cells. It plays a key role in cellular respiration by oxidizing acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, as well as electron carriers like NADH and FADH2. The conversion of fumaric acid to malic acid is one of the steps in this cycle, illustrating the importance of these transformations in energy metabolism.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 2:55m
2:55m